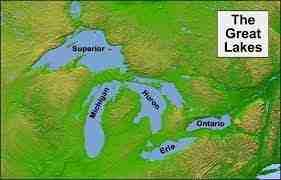
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America or the Laurentian Great Lakes, are a group of substantial interconnected freshwater lakes with specific sea-like characteristics within the middle-east area of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. They include Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario and are located close to or along the border between the US and Canada. From a hydrological perspective, the lakes of Michigan and Huron are one body, joined by the Straits of Mackinac. The Great Lakes Waterway allows modern shipping and travel by the water between the lakes.
The Great Lakes are the largest freshwater lake group on Earth in terms of area. They are the second largest in total volume, with 21 percent of the world’s surface freshwater volume. The total surface is the equivalent of 94,250 acres (244,106 km2), while the overall quantity (measured at the lowest water date) is 539 cubic miles (22,671 km3),[5approximately smaller than that in Lake Baikal (5,666 cu mi or 23,615 sq km, 22-23 percent of the world’s surface freshwater). Due to their characteristics that resemble seas that include continuous winds, rolling waves, strong currents, vast depths, and distant horizons, all five Great Lakes have long been described as”inland seas. Based on how they are measured, in terms of surface area, Lake Superior or Lake Michigan-Huron is the second-largest in the world. It is also one of the biggest freshwater lakes. Lake Michigan is the largest lake that is located in one country. [7][8][9][10]
The Great Lakes began to form towards the end of the Last Glacial Period around 14,000 years ago when melting ice sheets exposed the basins they cut into the Earth and filled with melting water. They are a significant source for transportation, migration, fishing, and trade, providing habitat for various aquatic species within an area rich in diversity. The area is known as”the Great Lakes region, which includes the Great Lakes Megalopolis. [12]
Physical characteristics
Geology
The age of the Great Lakes is still not definitively established. Estimates vary from 7,000 to 32,000 years old. The waters began to fill the glacially scoured basins as early as the ice receded around fourteen thousand years earlier. It is generally believed that Lake Erie reached its present levels around 10,000 years ago. Lake Ontario about 7,000 years ago, as well as Lakes Huron, Michigan, and Superior around 3,000 years ago.
Water glass with white background. (drink clear; clear; pure water or liquid)
Although water is found throughout three states, there’s only the correct solution to all the questions on this test. So, dive in, test your understanding of water, and test whether you can swim or sink.
The current configuration in the Great Lakes basin results from the passage of massive glaciers throughout the mid-continental region. The process began around a million years ago, during the Pleistocene Epoch. Research in The Lake Superior region indicates that the valleys and river systems created by water erosion existed before the Ice Age. The glaciers indeed explored the valleys, widening and deepening them. This led to radically altering the drainage patterns of the region.
The most recent glaciation in North America is called the Wisconsin Glacial Stage because it created several new landforms and sediments in the state. The first parts of the Great Lakes were created when the ice sheet began to melt and receded approximately 14,000 years before. Lake Chicago, in what is currently in the northern Lake Michigan basin, and Lake Maumee, in present-day western Lake Erie and its adjacent lowlands, were initially drained to the south towards the Mississippi River through the Illinois and Wabash drainages, respectively. When the retreat of the glaciers continued, Lake Maumee was drained into Lake Chicago through a valley now Lake Chicago, now the Grand River in Michigan. In the end, drainage to the east and towards the Atlantic Ocean was established, initially through the valleys formed by the Mohawk and Hudson rivers and later through the course of the lower St. Lawrence River. At one point, it was believed that the waters of the Huron and Michigan basin merged to form one colossal lake called Lake Algonquin. Then, Lake Duluth, in the western part of the Lake Superior basin, also drains.
D is up to Mississippi.
Various deposits and types of rocks can be located within the Great Lakes because of their vast area and glacial source. The old rock formations of the Canadian Shield comprise a portion of the Superior and the Huron basins, and Paleozoic sedimentary rocks comprise the remaining basins. The limestone is found in outcrops, as well as massive deposits of gravel and sand typically close to shore. Organic sediments and glacial clays are typical in the deeper areas.
Primary waterways that connect
Chicago, located on Lake Michigan, is in the western portion of the lake’s megalopolis. It is also the location of the waterway connecting the lakes with the Mississippi River valley.
Detroit along the Detroit River links the region’s central metropolitan areas.
The Chicago River and Calumet River systems link the Great Lakes Basin to the Mississippi River System through human-made changes and canals.
- The St. Marys River, comprising its Soo Locks, connects Lake Superior to Lake Huron via the North Channel.
- The Straits of Mackinac connect Lake Michigan to Lake Huron (which are hydrologically one).
- The St. Clair River connects Lake Huron to Lake St. Clair.
- The Detroit River connects Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie.
- The Niagara River, including Niagara Falls, links Lake Erie to Lake Ontario.
- The Welland Canal bypasses the Niagara River, connecting Lake Erie to Lake Ontario.
The Saint Lawrence River and the Saint Lawrence Seaway connect Lake Ontario to the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, which connects with the Atlantic Ocean.
Lake Michigan-Huron
Lake Michigan-Huron, with north orientation to the right, was captured on the 14th of April, 2022, during Expedition 67 of the International Space Station. Green Bay is at the upper right, and Saginaw Bay is on the left.
Lakes Huron and Michigan are often referred to as a single lake, or Lake Michigan-Huron because they form one body of water linked by the Straits of Mackinac. The straits measure approximately five miles (8 km) wide and 120 feet (37 m) deep. The levels of the water change and then fall, while the flows that flow across Michigan and Huron often reverse direction.
Human impacts on lakes
The various uses of lakes can be conflicting. For example, hydroelectric power and shipping industries prefer higher water levels. At the same time, homeowners living along the shoreline are concerned that higher levels can cause more erosion along the coastline. Conservationists believe that diverting treated sewage from lakes, as it is happening in Chicago and urban areas, is the ideal method to ensure the health of the water. No matter what method is adopted, there is no doubt that there have been changes in the lake’s animal and aquatic plant life. It is also clear that these changes are caused by an increase in the number of chemicals introduced into the lakes, depletion of dissolved oxygen in certain areas, and the accumulation of sewage sludge at the bottoms of lakes near urban zones.
Significant changes began to be noticed around 1900 and coincided with the growth of the humans living around the lakes. In the years following, the misuse of the lakes was all too evident and was illustrated by the increasing number of beaches closed following 1950 due to pollution. However, the less apparent development of harmful substances in wildlife, mainly fish and birds that eat fish, was more significant. It was realized that pollution could affect directly or indirectly every use, increasing the price of water treatment, causing the death of important fish species, or making other species unfit for consumption and negatively affecting tourism and the value of property along shorelines. Since the 1970s, the authorities from Canada and the United States have undertaken a significant collaborative effort to control pollution. This has led to improvements in water quality and the revival of some fish populations.